Outbreak and spread of the novel coronavirus
Since the end of December 2019, a novel coronavirus has been spreading from the Hubei province in China and has reached many countries worldwide. Unlike an epidemic, which is a regionally occurring contagious disease, a pandemic is a worldwide epidemic that is the case of this novel coronavirus, named recently SARS-CoV-21), which causes the disease COVID-19. You can find an overview of the coronavirus-risk areas on the website of the WHO (World Health Organisation).
The virus spreads typically via small droplets which are spread when a person with COVID-19 coughs or exhales. Another person can then catch the virus by breathing in these droplets or touching objects contaminated by these droplets and then touching its eyes, nose or mouth2). The currently known incubation period is max. 14 days2).
What preventive measures to take
Containment can only be achieved through sensible behavior and the observance of general hygiene measures and especially of hand hygiene.
It is not clear how long the novel coronavirus remains infectious on surfaces and objects. Studies suggest that it may persist for at least a few hours and up to several days3). We suggest to clean objects regularly with disinfectant products.
How to reduce the risk of getting infected - tips for everyday life
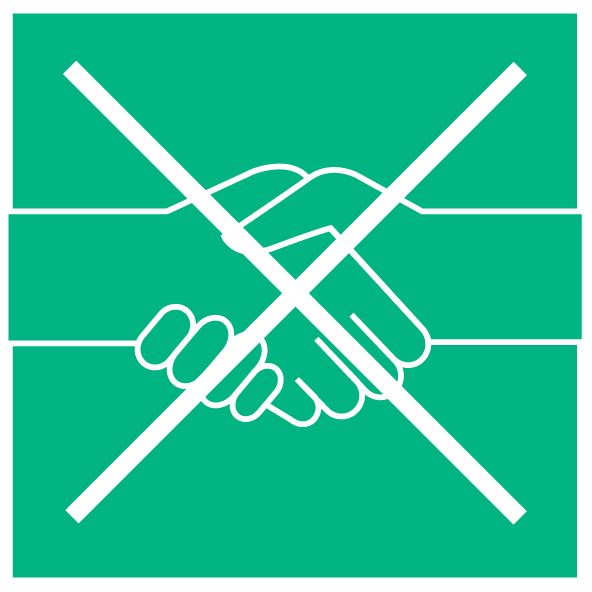
No handshaking or kissing on the cheeks
Even if it seems rude at first, refrain from shaking hands with each other. Avoid physical contact in general.
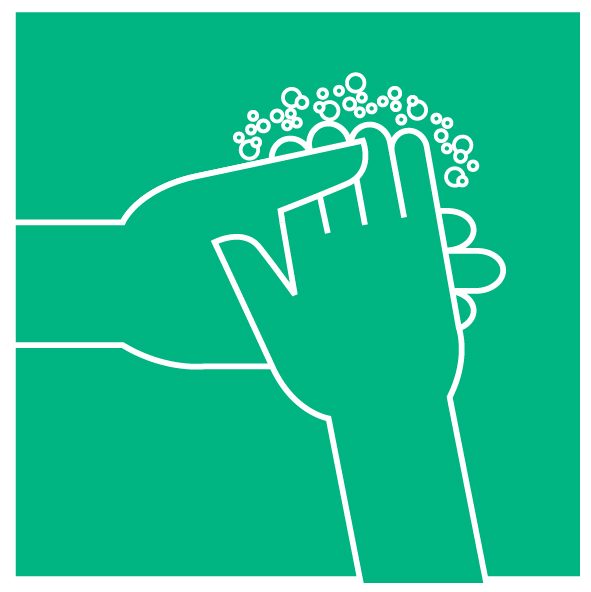
Clean your hands frequently
Clean your hands with an alcohol-based hand rub or wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water, especially before preparing food, before eating, or when you get home. Always wash your hands after using the toilet or if the hands are visibly dirty. Learn here how to wash or disinfect your hands properly.
Keep your hands away from your face
Pathogens can easily pass from the hands to the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, and mouth. Avoid touching your face.
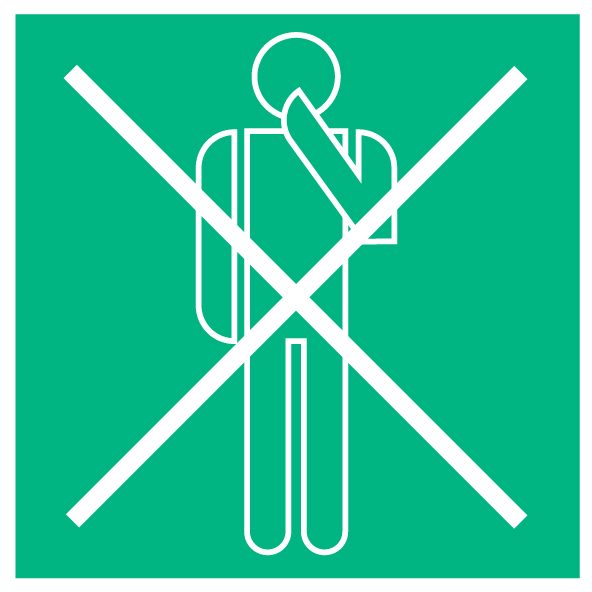
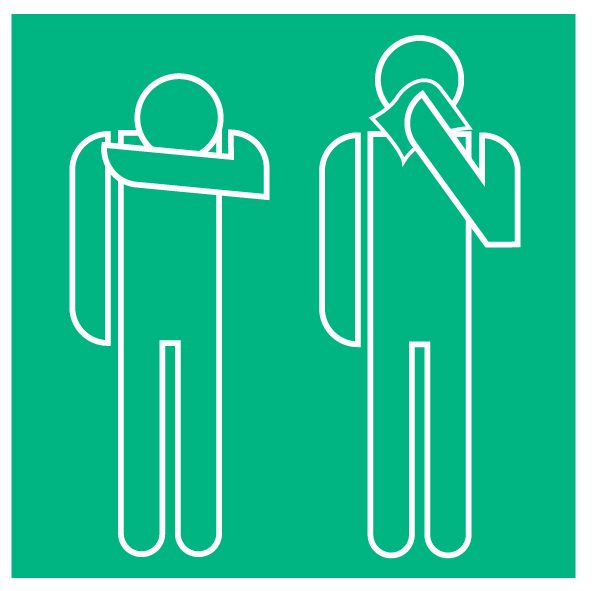
Hygienic coughing and sneezing
When coughing, “hand over mouth” is well intended, but in doing so you catapult a large number of viruses out of your body, which then stick to your hands. So do not cough into your hands, but rather into your sleeve or a tissue.
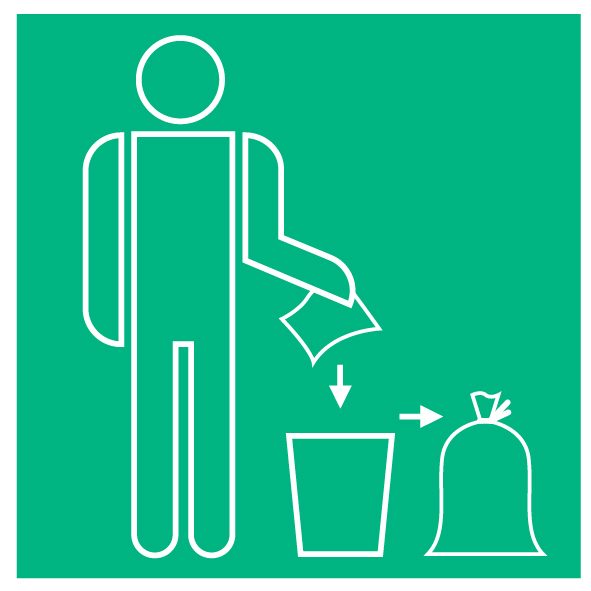
Discard used tissues immediately
Throw used tissues immediately into the trash – preferably into a container with a garbage bag that you can close tightly and dispose of regularly. Then please wash your hands.
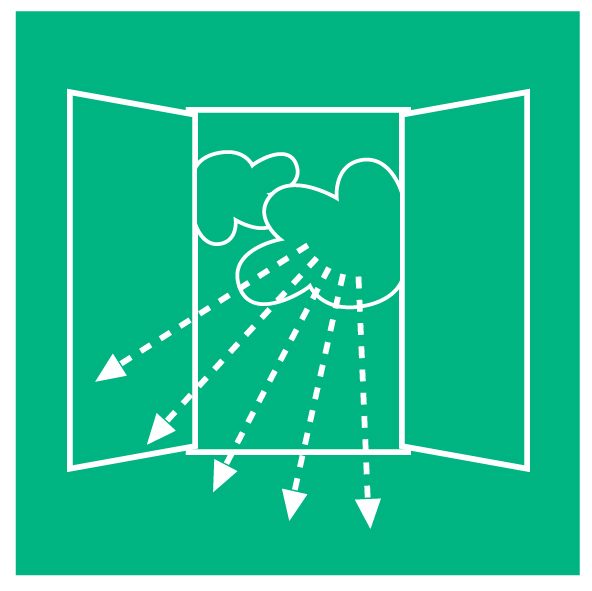
Ventilate regularly
In closed rooms, the number of viruses in the air can increase dramatically.
Regularly ventilating a room (three to four times a day for ten minutes) counteracts this and thereby reduces the risk of infection.
It also improves the indoor climate and prevents the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose from drying out.
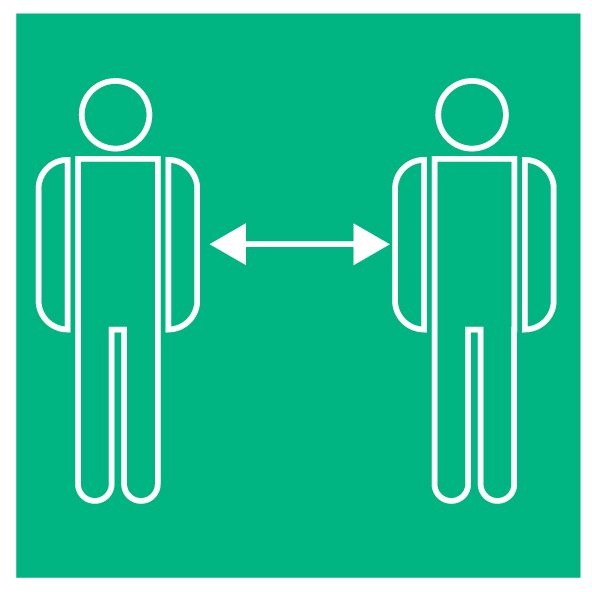
Keep your distance and avoid crowds
Keep the greatest possible distance from other people when coughing, at least 1 meter, to avoid breathing in droplets, which could include the novel coronavirus causing COVID-19, if the person is infected.
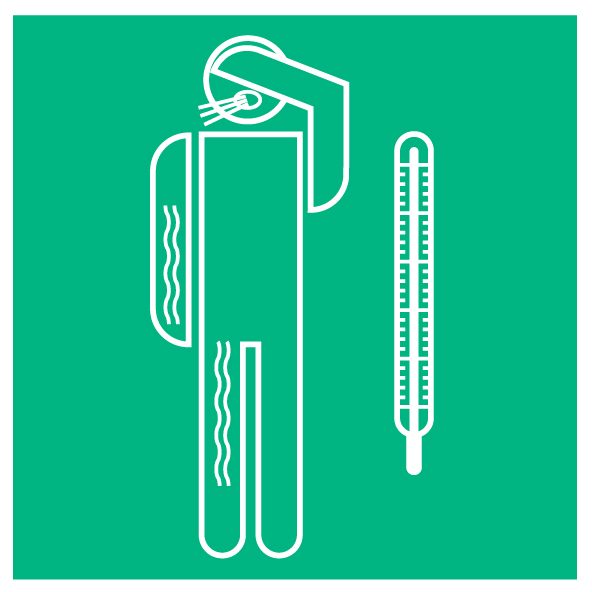
Pay attention to first symptoms
If you have a fever, cough, or difficulty breathing, see a doctor as soon as possible. Important: call beforehand so that you are directed straight to the right health facility and thus avoiding to get in touch with too many people. Follow the directions of your local health authority.
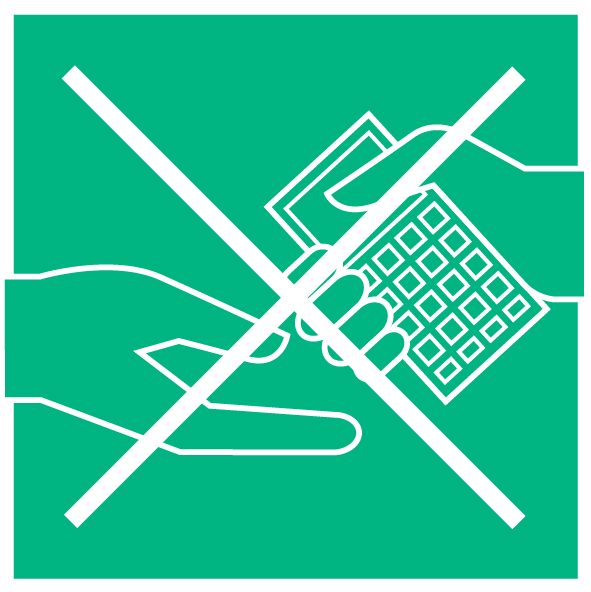
Do not share objects
Avoid sharing objects and touching surfaces in public spaces as it is known that the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19 remains on surfaces4). If you think an object may be infected, contaminated, clean it using a surface disinfectant followed by washing your hands.
Download
Be on the safe side - avoid touching surfaces
It is not yet clear how long the novel coronavirus remains infectious on surfaces and objects. Studies suggest that it may persist for up to several days4. Therefore, we suggest that you avoid touching objects and clean your hands regularly.
Keep these tips in mind if you need to leave the house
Avoid respiratory irritation when disinfecting surfaces successful
Disinfect surfaces evenly and avoid droplets and aerosols while using the spray or a flip-top bottle to wet a wipe or use an already pre-soaked wipe rather than spray directly on the surface. In addition, the surface is disinfected evenly and you avoid droplets and aerosols which helps to avoid respiratory irritations. Don’t forget to observe the exposure times.
Grocery shopping
There is no way around it: When you go grocery shopping, you touch surfaces and items, including trolleys and baskets. Clean your hands with an alcohol based handrub when entering and leaving the store. Avoid in any case touching your face while you are shoppping and wash your hands thoroughly as soon as you arrive home. Wash purchased vegetables and fruits with water and disinfect the surface of other bought items.
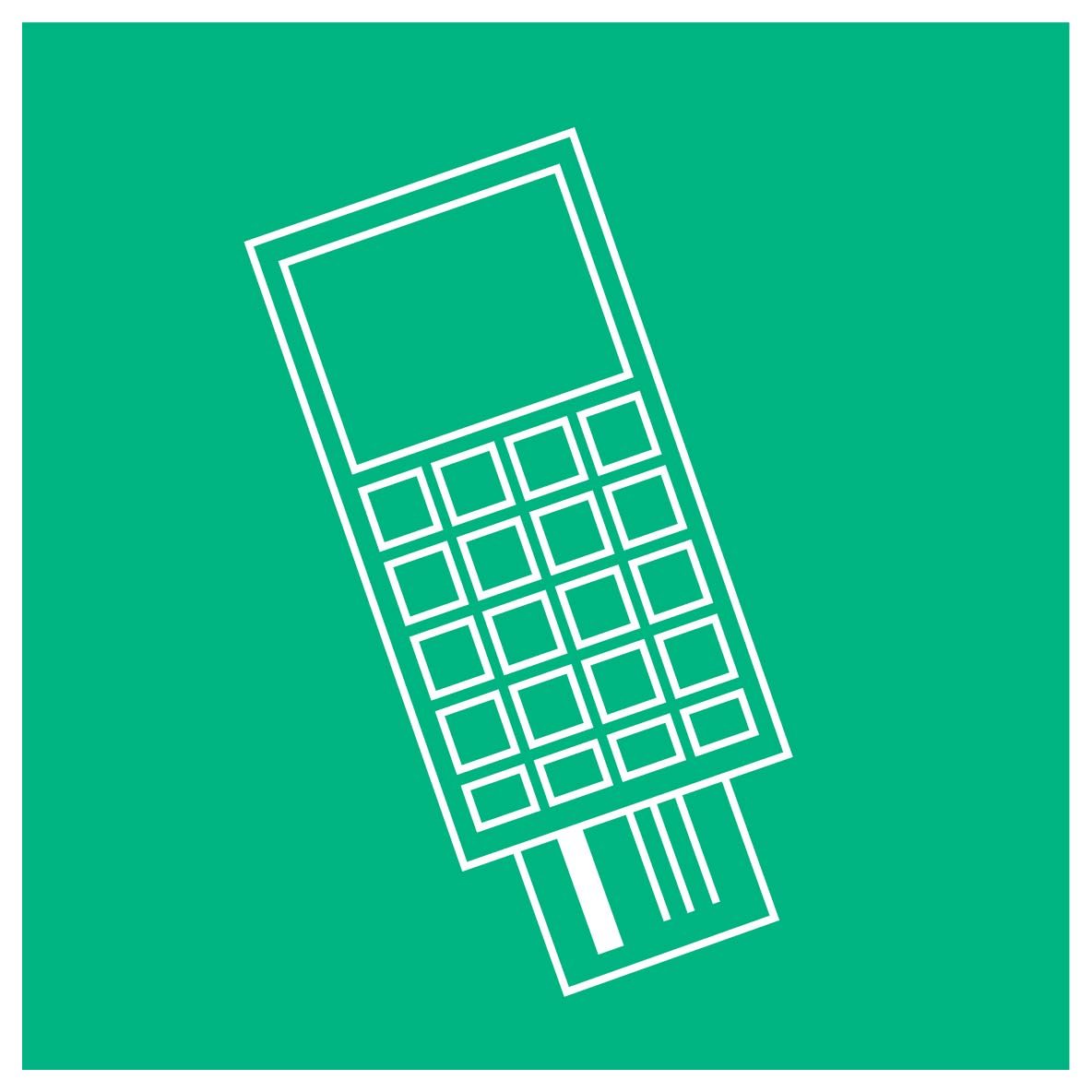
Making payments
Cards and cash could transfer the virus to your hands. However, card payment probably poses a lower risk, as you hold your own card and do not have to touch other people. Contactless bank transfers are also a good way to reduce any risk.
Objects in public
Frequently touched surfaces such as lift buttons and door handles in public places present a higher risk. We recommend that you avoid touching such surfaces by opening doors with your elbows or with your shoulder or using the stairs instead of the elevator whenever possible. After visiting the public bathroom, wash your hands with soap and water for 40 to 60 seconds. Also consider flushing the toilet with the lid lowered to prevent dropplets from being inhaled or contaminating close surfaces.
References:
1) "Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it"; https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technical-guidance/naming-the-coronavirus-disease-(covid-2019)-and-the-virus-that-causes-it
2) "How does Covid-19 spread?"; https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses
3) "How long is the incubation period of Covid-19? https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses
4) How long does the virus survive on surfaces? https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses